Greetings fellow astrophiles!
The September 27th Baltimore Woods session was notable for several reasons. On the down side, my drive to Marcellus through Fairmount was delayed when a minivan with far too many large dogs in it had one of its automatic windows dropped down to the delight of an ejected dog that bounced off my driver side door (my non-astro thought for the day – if your pets are your children, please use the child safety options built into your very modern vehicle!). On the up side, for the first time since March, a Baltimore Woods session started at 7 p.m. The skies were dark enough to begin seeing the brightest stars with ease and cold enough to freeze out the many bugs that frequent the BW Nature Center.
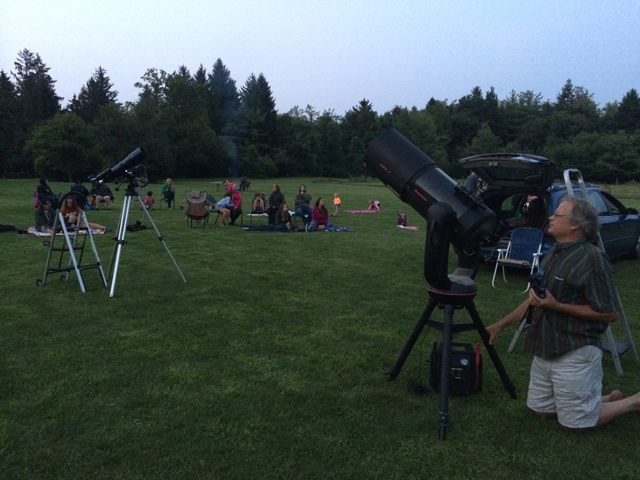
Attending scopes included Bob Piekiel‘s massive 16″ Meade GOTO (with some included heavy lifting by the two of us to get it set up and torn down), Larry Slosberg’s 12″ New Moon Telescope, and my 12.5″ NMT Dob (herein referred to as “Ruby”). A fourth scope appeared early in the evening with the first attending family, but ended up not getting too much use. Despite being a bit worse for wear, their “retail store” Stratus 60mm refractor scope surprised the owners (and kids) with a good view of a distant cellular tower and a fuzzy but noticeably “half-moon cookie” Venus (whatever description works is fine with me).

Bob inspecting the Stratus 60mm.
The final size (25ish) of the crowd (and the number of first-time attendees) dictated the observables for the evening, with all of us sticking mostly to bright, easily identifiable objects. As for our local neighborhood, the good news was that more than half of the planets were out for the evening (counting the views of Earth). The bad news was that Venus and Saturn set early (both due to the time and the high trees along the Western horizon), leaving the very distant Uranus and Neptune as targets for later-night observers.
As has been my standard procedure, I picked one object from my standard list of “kinds of” objects so those at my scope would be sure to get a sampling of the types of objects we amateur astronomers look forward to looking at. My list included:
* (Hopefully) One Planet – From my (scope’s) vantage point, Venus and Saturn were impossible catches behind large trees. Neptune and Uranus were, for the entire viewing session, nestled within the glow of Marcellus (and Syracuse beyond), so I didn’t even bother attempting to find them. Bob, however, had at his disposal a massive GOTO, so the gathered crowd was able to take in at least one of the two distant planets (making them part of the way-less-than-1% of the entire planet who can claim the same).
* One Star – At Bob’s request, I gave special attention to Herschel’s Garnet Star (mu Cephei) in Cepheus. One of the real benefits of magnification through good optics (or long-exposure photography) is the appearance of color in many stars that are otherwise just too slightly colored to be noticeable to Naked Eye observers. While the different colors of the binary star Albireo are generally obvious to most people, the Garnet Star jumped out to everyone through every eyepiece as a very orange star. This red supergiant, affectionately known to some as Erakis, is BIG. Those who have seen the image below in one of our CNYO library lectures…
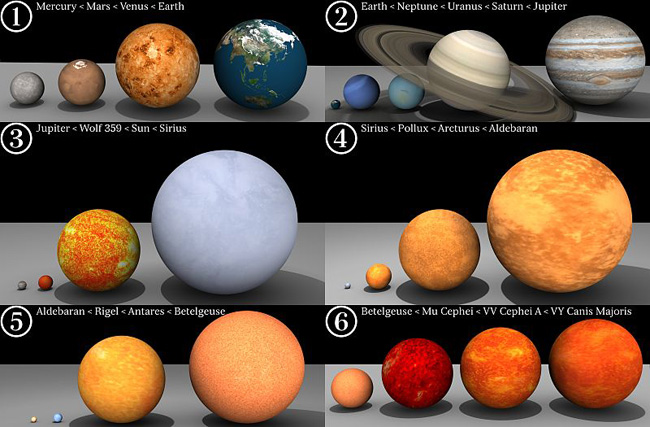

The scale of familiar objects in our vicinity (click for the wikipedia version).
Will recognize Mu Cephei as the third star from right (in the “Big Block” 6) in the bottom of the image. Our own Sun peters out in Block 3. If a super race of aliens were to swap out our Sun for the Garnet Star, the outer edge of its plasma would engulf Jupiter and either engulf or roast Saturn. Big. Not only big, but old to boot. Mu Cephei is what is known as a “carbon star,” one that has nearly exhausted its helium (which is produced from all the fusion of hydrogen, which it then exhausted quite some time ago) and is now producing carbon in the star’s core. The near-exhaustion of the star’s fuel means that it’s likely only a few million years from going supernova (somewhere between a finger snap and ringing wine glass in cosmic terms) and is currently identified as a variable star for its subtle and erratically changing brightness.
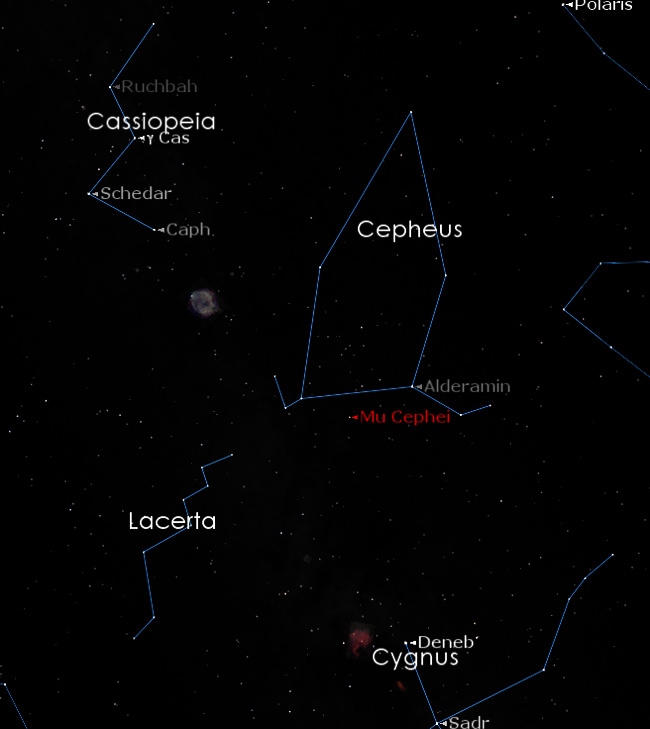
Mu Cephei, Cepheus, and surrounding constellations.
As you scour Cepheus some evening, do take the Garnet Star in. If you’re scanning randomly along the bottom of the barn, you can’t miss it!
* One Binary – Albireo in Cygnus remains an easy favorite. Everyone saw Albireo A as slightly orange or yellow, while Albireo B appeared as slightly to “clearly” blue (clearly a demonstration of the importance of dark adaption and cone sensitivity in the retina). One point of interest is that we’re not entirely sure of Albireo is an optical binary (the two just appear close, but one is much farther away than the other as projected onto our two-dimensional sheet of the Night Sky) or a gravitationally-bound binary pair. If gravitationally-bound, the two are likely far from one another, with the orbital dance occurring over 100,000 or more years.
* One Open Cluster – The Double Cluster (Caldwell 14) in Perseus
* One Globular Cluster – The ever-obvious M13 in Hercules
* One Nebula – The Veil Nebula in Cygnus – typically, this would be considered one of the less-easy objects for a new observer to make out. Through an OII filter, however, the wispy-ness jumps out and new observers, with a little patience, can even see the curvature of each fragment well enough to know where the Veil must be radiating from.
* One Galaxy – M31, The Andromeda Galaxy in Andromeda (and M32 and M110), which were easy for all to spot with a little scope nudging.
As has become the norm recently, I packed up Ruby around 9:30 p.m. and pulled out the Canon T3i and tripod for an extended session of scope-less astrophotography. Three highlights include a very discernible Milky Way, complete with Great Rift, from opposite the direction of Marcellus…

The Milky Way (plus one bright plane and one dim satellite). Click for a larger version.
A dimmer part of the Milky Way that seemed to radiate from (and be washed out by) Marcellus…

The Milky Way and Marcellus (plus a dim plane (dashed line) and dim satellite). Click for a larger version.
And a quite decent view of the varied objects in the vicinity of the constellation Perseus (in the pocket between the two trees and closer to the left tree), including the components of the Double Cluster, NGC 884 and 869 (the fuzzy splotches at the base of the small necklace – 1/3 over from the left edge and 1/4 down the image).
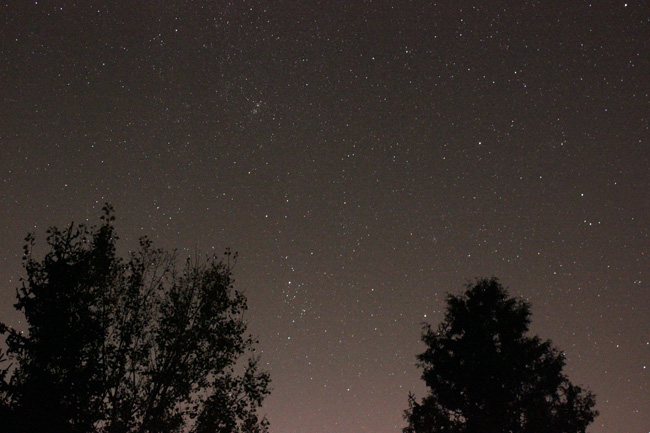

Perseus, NGC 884, and NGC 869. Click for a larger version.
I packed it in around 10:00 p.m. in great anticipation! Within the glow of Marcellus lay the Pleiades (M45) and just a hint of its closer cousin the Hyades in the head of Taurus the Bull. These objects have likely served as markers for many millennia that the clear, dark, steady, and uncomfortably cold night skies of winter approach.